ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS:
1. Find the area of the circle inscribed in a square of side a cm.
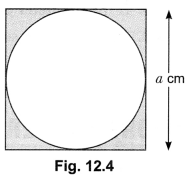
Soln:
Diameter of the circle = a
![]()
2. Find the area of a sector of a circle whose radius is and length of the arc is l.
Soln:
Area of the sector of the circle with radius r
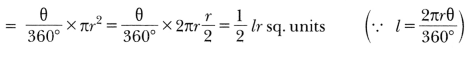
3. Find the ratio of the areas of a circle and an equilateral triangle whose diameter and a side are respectively equal.
Soln:
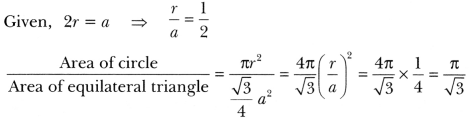
4. A square inscribed in a circle of diameter d and another square is circumscribing the circle. Show that the area of the outer square is twice the area of the inner square.
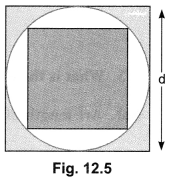
Soln:
Side of outer square = d {Fig. 12.5]
∴ Its area = d
Diagonal of inner square = d
∴ Side = d /√2
⇒ Area = d²/2
Area of outer square = 2 × Area of inner square.
5. If circumference and the area of a circle are numerically equal, find the diameter of the circle.
Soln:
Given, 2πr = πr2
⇒ 2r = r2
⇒ r(r – 2) = 0 or r = 2
d = 4 units
6. The radius of a wheel is 0.25 m. Find the number of revolutions it will make to travel a distance of 11 km.
Soln:
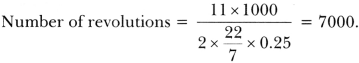
7. If the perimeter of a semi-circular protractor is 36 cm, find its diameter.
Soln:
Perimeter of a semicircular protractor = Perimeter of a semicircle
= (2r + πr) cm
⇒ 2r + πr = 36
⇒ r(2+227) = 36
⇒ r = 7cm
Diameter 2r = 2 × 7 = 14 cm.
8. If the diameter of a semicircular protractor is 14 cm, then find its perimeter.
Soln:
Perimeter of a semicircle = πr + 2r
= 227 × 7 + 2 × 7 = 22 + 14 = 36 cm
9. If a square is inscribed in a circle, what is the ratio of the areas of the circle and the square?
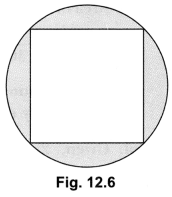
Soln:
Let radius of the circle be r units.
Then, diagonal of the square = 2r
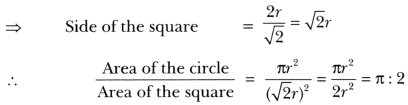
10. What is the area of the largest triangle that is inscribed in a semi circle of radius r unit?
Soln:
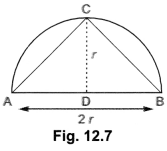
Area of largest ∆ABC = 12 × AB × CD
12 × 2r × r = r2 sq. units
11. What is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 10 cm by an arc of length 5π cm?
Soln:
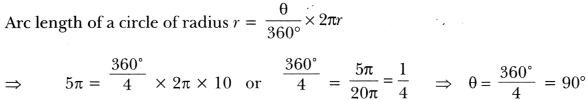
12. Difference between the circumference and radius of a circle is 37 cm. Find the area of circle.
Soln:
Given 2π r – r = 37
or r (2π – 1) = 37
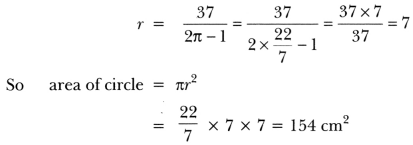
13. The radii of two circles are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle having area equal to the sum of the areas of the two circles.
Soln:
Let r be the radius of required circle. Then, we have
πr2 = π(8)2 + π(6)2
⇒ πr2 = 64π + 36π
⇒ πr2 = 100π
∴ r2 = 100ππ = 100
⇒ r = 10cm
Hence, radius of required circle is 10 cm.
14. The area of a circular playground is 22176 m2. Find the cost of fencing this ground at the rate of Rs 50 per m.
Soln:
Area of circular playground = 22176 m2
πr2 = 22176
⇒ 227 r2 = 2176
⇒ 22176 × 722
⇒ r = 84 m
∴ Circumference of the playground =2πr = 2 × 227 × 84 = 44 × 12 = 528 m .
∴ Cost of fencing this ground = Rs 528 × 50 = Rs 26400.
15. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes.
Soln:
Since the minute hand rotates through 6° in one minute, therefore, area swept by the minute hand in one minute is the area of a sector of angle 6° in a circle of radius 14 cm.
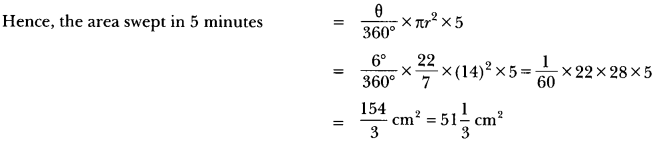
16. To warn ships for underwater rocks, a lighthouse spreads a red coloured light over a sector of angle 80° to a distance of 16.5 km. Find the area of the sea over which the ships are warned. (Use π = 3.14)
Soln:
We have, r = 16.5 km and 0 = 80°
∴ Area of the sea over which the ships are warned =
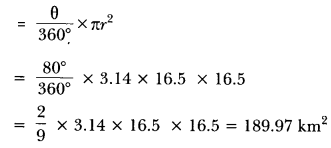
17. A race track is in the form of a ring whose inner circumference is 352 m, and the outer circumference is 396 m. Find the width of the track.
Soln:
Let the outer and inner radii of the ring be R m and r m respectively. Then,
2πR = 396 and 2πr = 352
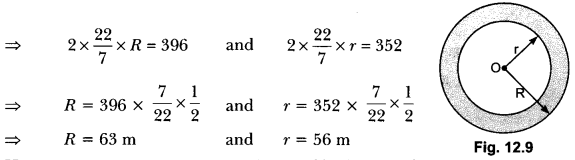
Hence, width of the track = (R – r) m = (63 – 56) m = 7 m
18. The wheels of a car are of diameter 80 cm each. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is travelling at a speed of 66 km per hour?
Soln:
The diameter of a wheel = 80 cm.
radius of the wheel = 40 cm.
Now, distance travelled in one complete revolution of wheel = 2π × 40 = 80π
Since, speed of the car is 66 km/h
So, distance travelled in 10 minutes = 66×100000×1060
= 11 × 100000 cm = 1100000 cm.
So, Number of complete revolutions in 10 minutes
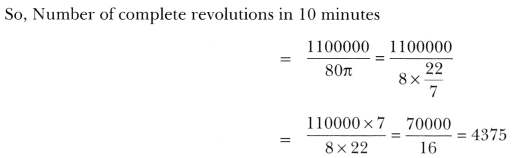
19. An umbrella has 8 ribs which are equally spaced (Fig. 12.11). Assuming umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella.
Soln:
We have, r = 45 cm
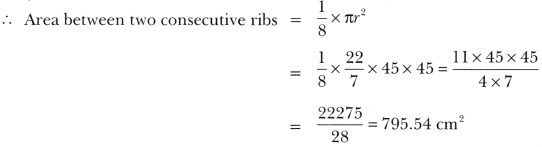
20. A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 25 cm sweeping through an angle of 115o. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades.
Soln:
We have, r = 25 cm and θ = 115°.
∴ Total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades
= 2 × (Area of the sector having radius 25 cm and angle θ = 115°).
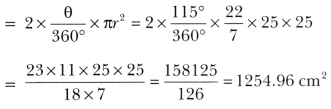
21. Find the area of a square inscribed in a circle of diameter p cm.
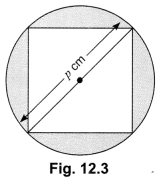
Soln:
Diagonal of the square = p cm
∴ p2 = side2 + side2
⇒ p2 = 2side2
or side2 = p22 cm2 = area of the square
22. The minute hand of a clock is 10 cm long. Find the area of the face of the clock described by the minute hand between 9 AM and 9.35 AM.
:Soln:
We have,
Angle described by the minute hand in one minute = 6°
∴ Angle described by the minute hand in 35 minutes = (6 × 35)° = 210°
Area swept by the minute hand in 35 minutes = Area of a sector of a circle of radius 10 cm
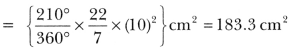
23. A round table cover has six equal designs as shown in Fig. 12.19. If the radius of the cover is 28 cm?, find the cost of making the designs at the rate of ₹ = 0.35 per cm2. (Use √3 = 1.7)
Soln:
Area of one design = Area of the sector OAPB – Area of ΔAOB
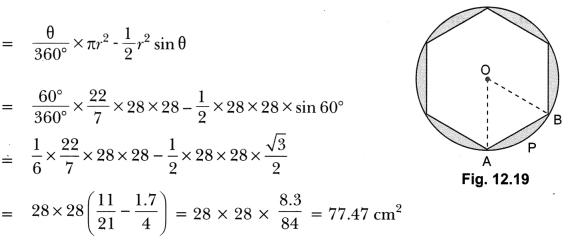
Area of 6 such designs = 77.47 × 6 = 464.8 cm2
Hence, cost of making such designs = ₹ 162.69
24. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 12.21, if radii of the two concentric circles with centre 0 are 7 cm and 14 cm respectively and ∠AOC = 40°.
Soln:
Area of shaded region
= Area of sector AOC – Area of sector OBD
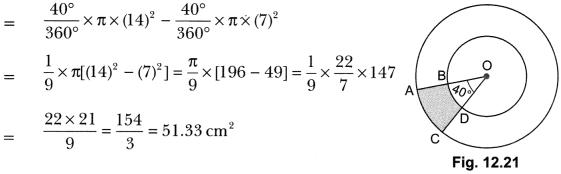
25. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig. 12.22, if ABCD is a square of side 14 cm and APD and BPC are semicircles.
Soln:
We have, radius of semicircles = 7 cm
∴ Area of shaded region
= Area of square ABCD – Area of semi-circles (APD +BPC)
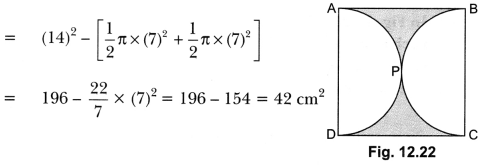
26. In Fig. 12.25, ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. With centres A, B, C and D, four circles are drawn such that each circle touches externally two of the remaining three circles. Find the area of the shaded region.
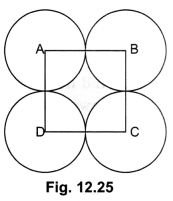
Soln:
We have, each side of square ABCD = 14 cm
∴ Area of square ABCD = (142)cm2 = 196 cm2
Now, radius of each quadrant of circle,
r = 142 = 7 cm
∴ The sum of the area of the four quadrants at the four corners of the square
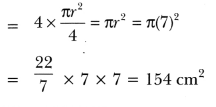
Now, area of shaded portion
= Area of square ABCD – The sum of the areas of four quadrants at the four corners of the square
= (196 – 154) cm2 = 42 cm2
