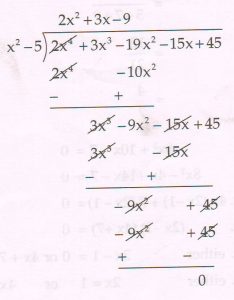Goa Board paper OCTOBER 2015
1 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
The sum of the zeros of the quadratic polynomial 6x2 − 4x + 3 is ______.
[ − \frac{3}{2} , − \frac{2}{3} , \frac{2}{3} , \frac{3}{2} ]
Ans: \frac{2}{3}
(B) By using Euclid’s division algorithm find the HCF of 12 and 28.
Ans: By division algorithm given by Euclid, we get
28 = 12 × 2 + 4
We again apply the division lemma to divisor 12 and remainder 4,
12 = 4 × 3 + 0
Since the remainder is 0, the process stops.
The divisor 4 here is the H.C.F of 12 and 28.
(C) Assuming that \sqrt{11} is an irrational number,
prove that: 2 + 3\sqrt{11} is also an irrational number.
Ans : Let us assume, to the contrary, that 2 + 3 \sqrt{11} is rational,
We can find coprime a and b ( where b ≠ 0 ) such that
2 + 3 \sqrt{11} = \frac{a}{b}
3 \sqrt{11} = \frac{a}{b} − 2
\sqrt{11} = \frac{a}{3b} − \frac{2}{3}
With a and b being integers, \frac{a}{3b} − \frac{2}{3} is rational
\sqrt{11} is rational, this contradicts the fact that \sqrt{11} is irrational
Our assumption that 2 + 3 \sqrt{11} is rational is false.
2 + 3 \sqrt{11} is irrational.
(D) If \sqrt{5} and − \sqrt{5} are the zeros of the polynomial 2x4 + 3x3 − 19x2 − 15x + 45 then find the other zeros.
Ans : Since \sqrt{5} and − \sqrt{5} are the zeros of the polynomial,
x − \sqrt{5} and x + \sqrt{5} are the factors of the polynomial
( x − \sqrt{5} ) ( x + \sqrt{5} ) = x2 − 5 is a factor.
The other factor is2x2 + 3x − 9
= 2x2 + 6x − 3x − 9
= 2x ( x + 3 ) − 3 ( x + 3)
= ( x + 3 ) (2x − 3 )
To get the other zeros, put ( x + 3) ( 2x − 3) = 0
This gives x = − 3 and x =\frac{3}{2}
The other zeros are − 3 and \frac{3}{2}
2 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
If the probability of losing an event is 0.03, then the probability of winning an event is ____.
[ 0 , 0.97 , 1 , 1.03 ]
Ans : 0.97
(B) A box contains 5 red marbles, 7 black marbles and 9 white marbles. If only one marble is drawn at random from the box, find the probability of getting-
(i). A black marble
Ans : Let E be the event of getting a black marble,
P (E) = \frac{Number \thinspace \thinspace of \thinspace \thinspace outcomes \thinspace \thinspace Favourable \thinspace \thinspace to \thinspace \thinspace E}{Number \thinspace \thinspace of \thinspace all \thinspace \thinspace possible \thinspace \thinspace outcomes}
= \frac{7}{5} + 7 + 9
=\frac{7}{21}
= \frac{1}{3}
(ii). Not a white marble
Ans : Let F be the event of getting not a white marble
P (E ) = \frac{Number \thinspace \thinspace of \thinspace \thinspace outcomes \thinspace \thinspace Favourable \thinspace \thinspace to \thinspace \thinspace E}{Number \thinspace \thinspace of \thinspace all \thinspace \thinspace possible \thinspace \thinspace outcomes}
= \frac{( 5 + 7)}{( 5 + 7 + 9)}
= \frac{12}{21}
= \frac{4}{7}
(C) Find the roots of ANY ONE of the following quadratic equations :
1. 8x2 + 10x − 7 = 0
( By using factorization method)
Ans : 8x2 + 10x − 7 = 0
8x2– 4x + 14x − 7 = 0
4x ( 2x − 1 ) + 7 ( 2x − 1 ) = 0
( 2x − 1 ) ( 4x + 7 ) = 0
Either 2x − 1= 0 or 4x + 7 = 0
Either 2x = 1 or 4x = − 7
Either x = \frac{1}{2} or x = − \frac{7}{4}
Roots of the equation are \frac{1}{2} and − \frac{7}{4}
2. 3x2 + 2x − 8 = 0 (deleted portion)
( By using completing the square method)
Ans : 3x2 + 2x − 8 = 0
x2 + \frac{2}{3} x − \frac{8}{3} = 0
x2 + \frac{2}{3} x + \frac{1}{9} = \frac{8}{3} + \frac{1}{9}
( x + \frac{1}{3} )2 = 24 + \frac{1}{9}
= \frac{25}{9}
Taking sq. root, ( x + \frac{1}{3} = ± \frac{5}{3} )
x + \frac{1}{3} = \frac{5}{3} OR x + \frac{1}{3} = − \frac{5}{3}
x = 5 − \frac{1}{3} OR x = − 5 − \frac{1}{3}
x = \frac{4}{3} OR x = − \frac{6}{3} = − 2
Roots are \frac{4}{3} and − 2
(D) The speed of a motorboat in still water is 15 km/ hr. It takes 1 hour less while returning 20 km downstream than while going 20 km upstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream.
Ans : Let the speed of the stream be x km / hr
Speed of the motor boat is 15 km / hr
Speed upstream is 15 − x
Speed downstream is 15 + x
\frac{20}{15 + x} − \frac{20}{15 − x} = 1
20 ( 15 + x ) − 20x (15 − x) = ( 15 − x ) ( 15 + x )
300 + 20x − 300 + 20x = 225 − x2
40x + x2 − 225 = 0
x2 + 40x − 225 = 0
x2 + 45x − 5x − 225 = 0
x ( x + 45 ) − 5 ( x + 45 ) = 0
( x + 45 ) ( x − 5 ) = 0
x = − 45 x = 5
x = − 45 is discarded
Speed of the stream is 5 km / hr.
3 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
If x = 7 and y = 3 is the solution of equations ax + by = 18 and bx + ay = 12 then a + b = ____.
[ − 7 , − 3 , 3 , 7 ]
Ans : 3
(B) The following is a pair of linear equations in two variables:
3x + 5y = 7
6x + ky = 3
Answer the following questions with reference to the given pair of equations.
1. Write down the conditions for a unique solution.
Ans : \frac{3}{6} ≠ \frac{5}{k} for a unique solution
k ≠ 10
2. Find the value of k.
Ans : 3k ≠ 30
k ≠ 10
k takes all values except 10
(C) Find the solution of ANY ONE of the following Linear equations :
1. 4x + 3y = 3 ; 7x − 5y = − 46
( By using elimination method )
Ans: 4x + 3y = 3 …. (1)
7x − 5y = − 46 …. (2)
Eq.(1) × 5, 20x + 15y = 15
Eq.(2) × 3, 21x − 15y = − 138
_____________
Subtracting 41x = − 123
x = − 3
Substituting x = − 3 in eq (1),
We get 4 × ( − 3) + 3y = 3
3y = 3 + 12
3y = 15
y = \frac{15}{3}
= 5
The solution is x = − 3 , y = 5
2. x − 2y = 4 ; 3x + 5y = 1
( By using substitution method)
Ans : x = 4 + 2y …. (1)
3x + 5y = 1 … (2)
Substituting x by eq (1) in eq (2)
3 ( 4 + 2y ) + 5y = 1
12 + 6y + 5y = 1
11y = 1 − 12
y = − \frac{11}{11}
= − 1
Substituting the value of y in eq. (1), we get
x = 4 + 2 ( − 1)
= 4 − 2 = 2
Solution is x = 2, y = − 1
(D) Find the solution of the following pair of linear equations graphically.
2x + y = 1 and x − 3y = − 17
Rewrite and complete the following tables
2x + y = 1
|
x |
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
x − 3y = − 17
|
x |
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
( Plot at least 3 points for each line using a graph paper)
Ans: 2x + y = 1
|
x |
0 |
1 |
−2 |
|
y= 1− 2x |
1 |
−1 |
5 |
x − 3y = − 17
|
x |
1 |
4 |
−2 |
|
y = \frac{x + 17}{3} |
6 |
7 |
5 |
Graphical solution is x = − 2, y = 5
4 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
The common difference of the A.P : 18 , 27 , 36 , …… is _____.
[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 11 ]
Ans : 9
(B) The daily income ( in Rs) of 30 workers of a factory was recorded as given below.
|
Daily income (in Rs) |
Number of workers |
|
600 − 700 |
6 |
|
700 − 800 |
8 |
|
800 − 900 |
10 |
|
900 − 1000 |
6 |
Find the median of the given data
Ans : Here n = 30 \frac{n}{2} = 15
The class, whose cumulative frequency is nearest to 15, is 800 − 900
800 − 900 is the median class
Now Median = l + [ \frac{n}{2} - \frac{Cf}{f} ] × h
Where
l = lower limit of the median class = 800
h = class size = 100
f = frequency of the median class = 10
Cf = Cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class = 8
Median = 800 + [ 15 − \frac{8}{10} ] × 100
= 800 + (\frac{7}{10} × 100)
= 800 + 70
= Rs 870
( C) After a survey, the Government decides to build 1450 houses in a village. In the first year the Government decides to build 25 houses and thereafter every successive year it will increase the number of houses to be built by 5.
Find the total number of years required by the Government to build all 1450 houses.
Ans : Let the required number of years be n
S = \frac{n}{2} [ 2a + (n − 1) d ]
1450 = \frac{n}{2} [ 2 × 25 + (n – 1) × 5 ]
2900 = n [ 50 + (n − 1) 5 ]
2900 = n [ 50 + 5n − 5 ]
2900 = 45n + 5n2
Dividing by 5,
n2 + 9n − 580 = 0
( n + 29 ) ( n − 20 ) = 0
Either n + 29 = 0 or n − 20 = 0
n = − 29 n = 20
Since number of years cannot be negative,
− 29 is discarded
Total number of years required is 20
(D) The following table shows the ages in years of 30 workers.
Taking the class mark denoted by ‘a’ of interval 36 − 42 as the assumed mean, rewrite and complete the table and also find the mean of the ages obtained by the assumed mean method.
Ans :
By assumed mean method
x = a + \frac{∑fidi}{∑fi}
= 39 + \frac{− 60}{30}
= 39 − 2 = 37
5 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
RS and RV are tangent segments drawn from external point R to the circle with center O at S and V respectively.
If ∠SOV = 110° then ∠ VRS = ___.
[ 35° , 45° , 55° , 70° ]
Ans : 70°
(B) Given : Point A is the centre of a circle.
GT and DT are two tangent segments drawn from external point T to the circle at G and D respectively.
Prove : GT = DT
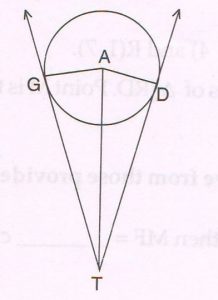
Proof :
Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are at right angles to the radii at the point of contact.
∠ AGT = ∠ ADT = 90°
In right Δs AGT and ADT
AT = AT ( common side)
AG = AD ( radii of the same circle )
Δ AGT Δ ADT ( Hypotenuse- side theorem)
GT = DT ( c.p.c.t )
( C) Draw a line segment MF of length 8.3 cm. Taking M as center draw a circle of radius 2.7 cm. Using a pair of compass and ruler, construct two tangents FX and FY to the circle. Measure and state the lengths of the tangent segments.
Ans :
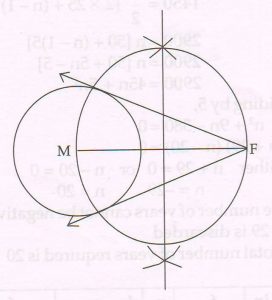
The length of each tangent segment is 7.7 cm
(D) Using a pair of compass and ruler construct Δ BEK with sides EK = 6.1 cm , BK = 5.3 cm and BE = 3.4 cm. Then construct Δ B’EK’ whose sides are\frac{5}{3} of the corresponding sides of Δ BEK.
Ans :
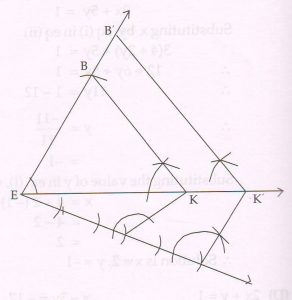
Δ B’EK is the required triangle whose sides are \frac{5}{3}of the corresponding sides of Δ BEK.
6 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
If sinA/ cos 76° = 1, where A is an acute angle then the value of A = ____.
[ 14° , 38° , 76° , 104° ]
Ans : 14°
(B) Attempt ANY ONE of the following :
1. In Δ QCF, ∠ C = 90° and cot F = \frac{ \sqrt{5} }{2} , then find :
(a) The length of QE
(b) The value of sec Q
(c) The value of cos F
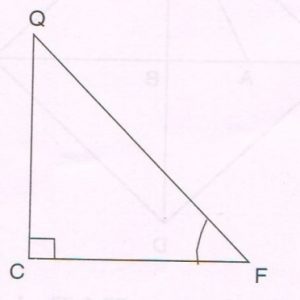
Ans :(a) By Pythagoras theorem
QF2 = QC2 + CF2
= ( 2k)2 + ( k )2
= 4k2 + 5k2
= 9k2
QF = \sqrt{9k}²
= 3k
(b) sec Q = \frac{1}{cosQ} = \frac{1}{ \frac{2k}{3k} } = \frac{3}{2}
(c) cos F = \frac{ \sqrt{5k} }{3k} = \frac{ \sqrt{5} }{3}
2. Evaluate the following expression using the known numerical values of trigonometrical ratios:
\frac{4}{3} cot2 30° + \frac{1}{3} cos2 45° − 3/4 cosec2 60°
Ans : \frac{4}{3} cot2 30° + \frac{1}{3} cos2 45° − \frac{3}{4}cosec2 60°.
= \frac{4}{3} × ( \sqrt{3} )2 + \frac{1}{3} ( \frac{ 1 }{ \sqrt{2} } )2 − \frac{3}{4} × ( \frac{2}{ \sqrt{3} } )2
= \frac{4}{3} × 3 + \frac{1}{3} × \frac{1}{2} − \frac{3}{4} × \frac{4}{3}
= 4 + \frac{1}{6} − 1
= 3 + \frac{1}{6}
= \frac{19}{6}
(C) Prove the following trigonometric identity :
( 1 − sin A ) ( sec A + tan A ) = cos A
Ans : L.H.S. = ( 1 − sin A) ( sec A + tan A)
= (1 − sin A) [ \frac{1}{cos A} + \frac{sin A}{cos A} ]
= ( 1 − sin A) [ \frac{1 + sinA}{cos A} ]
= 1 − \frac{sin² A}{cos A}
= \frac{cos² A}{cos A}
= cos A
= R.H.S.
(D) Attempt each of the following :
1. Find the distance between the points F ( − 2, 4 ) and R ( 1 , 7 ).
Ans : FR = \sqrt{(- 2 - 1)²+ ( 4- 7)²}
= \sqrt{ 9 + 9}
= \sqrt{18}
= 3 \sqrt{2}
2. R (− 4 , 2 ) , J ( 2 , 6 ) and D ( 0, − 4 ) are the vertices of ΔJRD. Point M is the midpoint of base DJ. Find the area of Δ RMJ.
Ans :
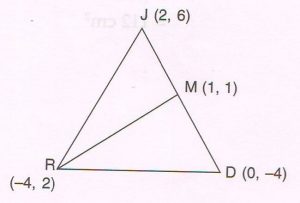
Coordinates of M
= [ 2 + \frac{0}{2} , 6 − \frac{4}{2} ]
= ( 1 , 1)
Area of Δ RMJ
= \frac{1}{2} [ − 4 ( 1 − 6) + 1 ( 6 − 2) + 2 (2 − 1) ]
= \frac{1}{2} [ 20 + 4 + 2 ]
= \frac{1}{2} × 26
= 13 square units
7 (A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
If Δ TVS ∼ ΔMPF ,ar ( TVS ) = 25 cm2
ar( MPF ) = 36 cm2 and TS = 15 cm, then MF = ____ cm.
[ 5 , 6 , 12 , 18 ]
Ans : 18
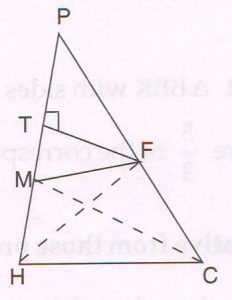
(B) With reference to the given figure and given condition, write only the proof with reasons of the following theorem.
Given : In ΔPHC, MF \| HC such that
P − M − H and P − F − C
FT ⊥ PH
Prove : \frac{PM}{MH} = \frac{PF}{FC}
ar ( PMF) = \frac{1}{2} × PM × FT
ar ( HMF) = \frac{1}{2} × MH × FT
Let MS ⊥ PC
ar (PMF) = \frac{1}{2} × PF × MS
and ar ( CFM) = \frac{1}{2} × CF × MS
\frac{ar ( PMF)}{ar (HMF)}
= \frac{ \frac{1}{2}×PM× FT }{ \frac{1}{2} ×MH ×FT }
= \frac{PM}{MH} … (1)
\frac{ar ( PMF)}{ar (CMF)}
= \frac{ \frac{1}{2}×PM × MS }{ \frac{1}{2}×CF × MS }
= \frac{PF}{FC} … (2)
Now ΔHMF and ΔCFM are on the same base HC and between the same parallels HC and MF
ar ( HMF ) = ar ( CFM) …. (3)
\frac{PM}{MH} = \frac{PF}{FC}
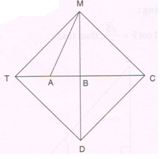
(C) In the given figure, MTDC is a rhombus. Diagonals MD and TC intersect at B. A is any point on TB, such that T – A – B.
Prove that: TD2 − MA2 = TA × AC
Proof: Since MTDC is a rhombus, diagonals bisect at right angles.
TD2 = TB2 + BD2 ( Pythagoras thm to ΔTBD )
MA2 = AB2 + MB2
TD2 − MA2 = TB2 + BD2 − AB2 − MB2
( Since MB = BD )
= ( TA + AB)2 − AB2
= TA2 + 2TA × AB + AB2 − AB2
= TA ( TA + 2AB )
= TA ( TA + AB + AB )
= TA ( TB + AB )
= TA ( BC + AB )
( Since TB = BC )
= TA × AC
(D) A boy stands between a pillar AF and a tower TM. The boy at B observes his father standing on the top T of the tower at an angle of elevation of 45°. At the same time, his father observes the top A of the pillar at an angle of depression of 30°. The boy is 75 m away from the foot of the tower. If the height of the pillar is 15 m then find the distance between the tower and the pillar.
( Take \sqrt{3} = 1.73 )
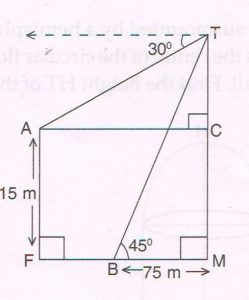
Ans : To find FM
Let TM = x meters
Now tan 45° = \frac{TM}{BM} = \frac{x}{75}
1 = \frac{x}{75}
TM = x = 75 meters
TC = TM − CM
= 75 − 15
= 60 meters
Also tan 30° = \frac{TC}{AC}
\frac{1}{ \sqrt{3} } = \frac{60}{AC}
AC = 60 \sqrt{3}
= 60 × 1.73
= 103.80
FM = AC
= 103.80 m
The distance between the tower and the pillar is 103.80 meters.
8 ( A) Select and write the most appropriate alternative from those provided in the bracket :
1. The cost of putting a fence around a circular field is Rs 5280 at the rate of Rs 24 per meter. Therefore the circumference of the circular field is ___ meters.
[ 22 , 110 , 220 , 270 ]
Ans : 220
2. The total surface area of a cube is 294 cm2. Therefore the length of its side is ____ cm.
[ 7 , 49 , 24.5 , 11 ]
Ans : 7
(B) Attempt each of the following :
1. Find the area of the quadrant of a circle, O−AXB, the radius of which is 12 cm. ( Do not substitute the value of π )
Ans : Area of sector O−AXB
= \frac{Ø}{360} × π r2
= \frac{90}{360} × π × 12 × 12 cm2
= 36 cm2
2. A joker’s cap is shaded like the frustum of a cone. The radius of the larger open circular end is 13 cm and the radius of the smaller closed circular end is 7 cm. Its slant height is 14 cm. Find the curved surface area of the frustum. (Do not substitute the value of π )
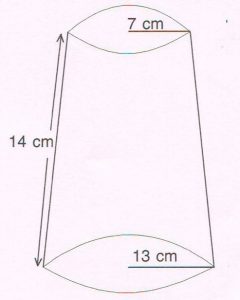
Ans : Curved surface area of the frustum
= π ( r1 + r2 ) × l
= π ( 7 + 13 ) × 14 cm2
= π × 20 × 14 cm2
= 280 π cm2
(C) In the adjoining figure, O is the center of the semicircle. Points A , C , D , Q are on the semicircle. AO is perpendicular to diameter CD. PORQ is a square.
OA = 14 cm then find the area of the shaded region.
( Take π = \frac{22}{7} )
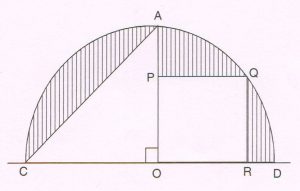
Ans : Area of the shaded region = area of semicircle
CAD − ar( sq. PORQ) − ar ( Δ AOC ) … (1)
Now OC = OD = OQ = OA = 14 cm
OQ = \sqrt{2} × OR
14 = \sqrt{2} × OR
OR = \frac{14}{ \sqrt{2} } cm
ar ( sq. PORQ) = \frac{14}{ \sqrt{2} } × \frac{14}{ \sqrt{2} } cm2
= 98 cm2 …. (2)
ar ( Δ AOC ) = \frac{1}{2} × OC × OA
= \frac{1}{2} × 14 × 14 cm
= 98 cm2 …. (3)
ar ( semicircle CAD )
= \frac{1}{2} π r2
= \frac{1}{2} × \frac{22}{7} × 14 × 14
= 308 cm2 …. (4)
From (1), (2), (3) and (4),
Area of the shaded region
= ( 308 − 98 − 98 ) cm2
= 112 cm2
(D) A hall is in the form of a cylinder surmounted by a hemispherical dome as shown in the figure. Its inner volume is 139.5 m3. Point T is the center of a circular floor. The internal diameter AB of the hall is equal to the height HT of the hall.
Find the height HT of the hall.
[ Take π = 3.1 ]
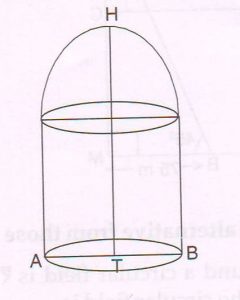
Ans : Let HT = x meters
AB = HT = x
AT = \frac{x}{2} meters
Inner volume = Volume of the cylinder + Volume of the hemisphere
139.5 = π × AT2 × ( x − \frac{x}{2} )+ \frac{2}{3} π × ( \frac{x}{2} )3
139.5 = 3.1 × \frac{x²}{4} × \frac{x}{2} × \frac{2}{3} × 3.1 × \frac{x²}{8}
139.5 = \frac{x²}{8} × 3.1 ( 1 + \frac{2}{3} )
x³ = 139.5 × 8 × \frac{3}{5} × \frac{1}{3.1}
= 9 × 8 × 3
= 33 × 23
x = 3 × 2 = 6
The height HT of the hall is 6 meters.