MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: (MCQ’s).
1. A circle has a ______number of tangents .
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) Infinite
2. The common point of the tangent and the circle is called the _____ .
(a) Point of contact
(b) Point of meeting
(c) Centre of circle
(d) None of the above
3. A circle can have _____ parallel tangents at a single time.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
4. If the angle between two radii of a circle is 110º, then the angle between the tangents at the ends of the radii is____
(a) 90º
(b) 50º
(c) 70º
(d) 40º
5. The length of the tangent from an external point A on a circle with centre O is ___
(a) Always greater than OA
(b) Equal to OA
(c) Always less than OA
(d) Cannot be estimated
6. If TP and TQ are the two tangents to a circle with centre O so that
∠POQ = 110°, then ∠PTQ is equal to _____
(a) 60°
(b) 70°
(c) 80°
(d) 90°
7. The length of a tangent from a point A at a distance 5 cm from the centre of the
circle is 4 cm. The radius of the circle is______
(a) 3 cm
(b) 5 cm
(c) 7 cm
(d) 10 cm
8. If a parallelogram circumscribes a circle, then it is a____
(a) Square
(b) Rectangle
(c) Rhombus
(d) None of the above
9. Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. The length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle is_____
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 18
10. Circles of this types are called _____
(a) Circular
(b) Concentric
(c) Normal
(d) None of the above
11. A line that intersects the circle at one point only is called ____
(a) Secant
(b) Chord
(c) Radius
(d) Tangent
12. The length of the tangent drawn from an external point to a circle are ____
(a) Equal
(b) Similar
(c) Not equal
(d) Parallel
13. The tangents drawn at the ends of the diameter of the circle are ____
(a) Equal
(b) Similar
(c) Not equal
(d) Parallel
14. The tangent to a circle is _____ the radius through the point of contact
(a) Equal
(b) Perpendicular
(c) Parallel
(d) None of the above
15. The parallelogram subscribing a circle is a ___
(a) Square
(b) Rectangle
(c) Rhombus
(d) Kite
1 :(d) ⇒ Textbook (Ex 10.1)
2 :(a) ⇒ Textbook ( Activity 2)
3 :(b) ⇒ Textbook (Ex 10.1)
4 :(a) ⇒ (Theorem 10.1)
5 :(c) ⇒ OA is the longest side.
6 :(b) ⇒ ∠POQ + ∠OPT + ∠OQT + ∠PQT = 360°
7 :(a) ⇒ Draw the fig and use Pythagoras theorem
8 :(c) ⇒ Tangents to a circle from an external point are equal
9 :(a) ⇒ Textbook (Example 1)
10 :(b) ⇒ Circles having common radius
11 :(d) ⇒ Definition tangent
12 :(a) ⇒ Textbook ( theorem 10.2)
13 :(d) ⇒ Draw and see
14 :(b) ⇒ Draw and see
15 :(c) ⇒ Textbook (example 10.2)
16 :(b) ⇒ Radius of bigger circle + difference of radius
17 :(d) ⇒ ∠AOB + ∠COD = 180°
18 :(c) ⇒ ∠ACB +∠ CBA +∠ BAC = 180° and∠ BAC +∠ BAT = 90°
19 :(a) ⇒ OP =13 cm ,OQ = OR = 5cm .Find area of the two Δs and add them
20 :(d) ⇒ Draw the fig .Let centre of CD be M and OM = 3 cm , OD = 5 cm (radius)
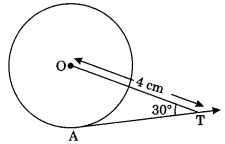
21 :(d) ⇒ Tan 30° = 4/x . So x = ?
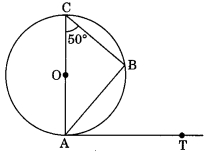
22 :(a) ⇒ ∠ OPQ =∠ OQP = 40° and ΔPOQ is isosceles
23 :(b) ⇒ ∠ APB +∠POB = 180°
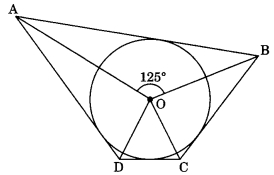
24 : (a) ⇒ ∠PSQ = 110° and so ∠POQ = 70° and …..
25 : (d) ⇒ ∠APB = 62° and so ∠AOB = 180°− 62 °
26: (d) ⇒ Angles around a point is equal to 360°
27: (b) ⇒ OP = √PQ²−OQ²
28: (c) ⇒ PQ = √ OQ²− PQ²
29: (c) ⇒ The chord AB touches the smaller circle at P. And OA² = OP² + AP²
30: (a) ⇒ AOC is its diameter
31: (b) ⇒ Draw the fig .Let centre of CD be M and OM = 3 cm , OD = 5 cm (radius)
32: (a) ⇒ OAT is a triangle and ∠OAT = 90°
33: (a) ⇒ OAB is a triangle. And ∠ OAB = ∠OBA
34: (d) ⇒ ∠OPR = 90°
35: (b) ⇒ Concentric circles definition