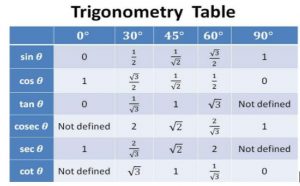
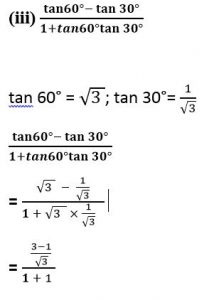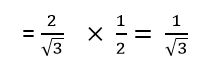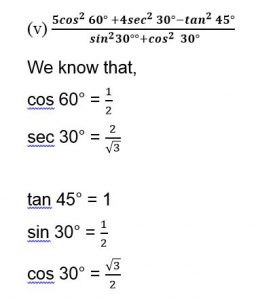TRIGNOMETRIC VALUES :
Use of Trigonometric Ratios and Table in Solving Problems:
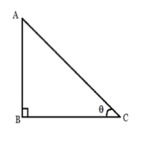
Example : Find the lengths of the sides BC and AC in ∆ ABC, right-angled at B where AB = 25 cm and ∠ACB = 30°, using trigonometric ratios.
Solution : To find the length of the side BC, we need to choose the ratio having BC and the given side AB. As we can see that BC is the side adjacent to angle C and AB is the side opposite to angle C, therefore
Tan C = AB/BC
Tan 30° = 25/BC = 1/√3
BC = 25√3 cm
To find the length of the side AC, we consider
Sin 30° = AB/AC
1/2= 25/AC
AC = 50 cm
Example 1: Evaluate the following:
(i) cosec 45° + tan 45° – 3 sin 90°
(ii) cos 60° cos 30° – sin 60° sin 30°
(iii) tan 60°−(tan 30°) / (1 + tan 60°tan 30°)
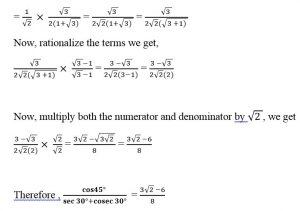
Solution: (i) cosec 45° + tan 45° – 3 sin 90°
cosec 45° =√ 2 ; tan 45° = 1; sin 90° = 1
∴ cosec 45° + tan 45° – 3sin 90° = (√2 + 1) – (3 × 1)
= √2 + 1 −3 ⇒ √2 −2
(ii) cos 60° cos 30° – sin 60° sin 30°
cos 60° = 1/2 : cos 30° = √3/2 ; sin 60° = √3/( 2) and sin 30° = 1/2
∴ cos 60° cos 30° – sin 60° sin 30°
= [ 1/2 × √3/2 ] – [ √3/2 × (1 )/2 ] = 0
(√3/4) −(√3/4) =0
Example 2: sin (A + B) = 1 and sin (A – B) = 1/2 ; where 0° < A + B ≤ 90°; ∠A > ∠ B.
Find ∠ A and∠ B.
Solution: sin (A + B) = 1
sin (A – B) = ( 1)/2
0° < A + B ≤ 90° and ∠A > ∠B
Compute A and B using sin (A + B) and sin (A – B)
sin (A + B) = 1
We know sin 90° = 1
∴ sin (A + B) = sin 90°
A + B = 90° ……(1)
sin (A – B) = ( 1)/2
∴ sin (A – B) = sin 30° (sin 30° = ½ )
A – B = 30° …… (2)
Add equations (1) and (2): (A + B) + (A – B) = 90° + 30°
2A = 120° ⇒ A = 60°
Substitute A = 60° in equation (1)
60° + B = 90°
Or B = 90° – 60° ⇒ B = 30°
So, ∠A = 60° and ∠B = 30°
EXERCISE 8.2
Solution: (i) sin 60° cos 30° + sin 30° cos 60°
First, find the values of the given trigonometric ratios
sin 30° = 1/2 : cos 30° = √3/2 : sin 60° = 3/2 : cos 60°= 1/2 :
Now, substitute the values in the given problem sin 60° cos 30° + sin 30° cos 60° = √3/2 × √3/2 + ( 1/2 ) × ( 1/2 )
= 3/4 + 1/4 = 4/4 = 1
2. Choose the correct option and justify your choice :
(i) (2tan 30°)/(1 + tan²30° ) =
(A) sin 60° (B) cos 60° (C) tan 60° (D) sin 30°
(ii) (1− tan²45°)/(1 + tan²45° ) =
(A) tan 90° (B) 1 (C) sin 45° (D) 0
(iii) sin 2A = 2 sin A is true when A =
(A) 0° (B) 30° (C) 45° (D) 60°
(iv) (2tan 30°)/(1− tan²30° )
(A) cos 60° (B) sin 60° (C) tan 60° (D) sin 30°
Solution: (i) (A) is correct.
Substitute the value of tan 30° in the given equation
(2 tan 30°)/(1+ (tan)² 30° = (2 (1/√3))/(1 + (1/(√3)²
= ((2/√3)/((1+ 1/3) ) = ((2/√3)/((4/(√3)
= 6/(4√3) = √3/2 = sin 60°
(ii) (D) is correct.
Substitute the value of tan 45° in the given equation
As sin 2A = sin 0° = 0
2 sin A = 2 sin 0° = 2 × 0 = 0
or,
Apply the sin 2A formula, to find the degree value
sin 2A = 2sin A cos A
⇒2sin A cos A = 2 sin A
⇒ 2cos A = 2 ⇒ cos A = 1
Now, we have to check, to get the solution as 1, which degree value has to be applied.
When 0 degree is applied to cos value, i.e., cos 0 =1
Therefore, ⇒ A = 0°
(iv) (C) is correct.
Substitute the of tan 30° in the given equation
Now, substitute the value of A in equation (i) to find the value of B
45° + B = 60°
B = 60° – 45°
B = 15°
Therefore A = 45° and B = 15°
4.State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A + sin B.
(ii) The value of sin θ increases as θ increases.
(iii) The value of cos θ increases as θ increases.
(iv) sin θ = cos θ for all values of θ.
(v) cot A is not defined for A = 0°.
Solution: (i) Let us take A = 30° and B = 60°, then
Substitute the values in the sin (A + B) formula, we get
sin (A + B) = sin (30° + 60°) ⇒ sin 90° = 1 and,
sin A + sin B = sin 30° + sin 60° ⇒ 1/2 + √3/2 ⇒ (1 + √3)/2
Since the values obtained are not equal, the solution is false.
(ii) sin 0° = 0 ; sin 30° = 1/2 ; sin 45° = 1/√2;
sin 60° = √3/2 ; sin 90° = 1
Thus the value of sin θ increases as θ increases. Hence, the statement is true
(iii) cos 0° = 1 ; cos 30° = √3/2 ; cos 45° = 1/√2 ;
cos 60° = 1/2 ; cos 90° = 0
Thus, the value of cos θ decreases as θ increases. So, the statement is false.
(iv) sin θ = cos θ, when a right triangle has 2 angles of (π/4). Therefore, the above statement is false.
(v) cot A = (cos A)/(sin A )
Now substitute A = 0°
cot 0° = (cos 0°)/(sin 0° ) = 1/0 = undefined.
Hence, it is true