INTRODUCTION:
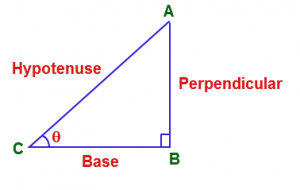
To find the distances and heights we can use the mathematical techniques, which come under the chapter Trigonometry. It shows the relationship between the sides and the angles of the triangle. Generally, it is used in the case of a right angled triangle.
sin\quad A\quad =\quad \frac { bc }{ ac } =\frac { perpendicular }{ hypotenuse } =\frac { p }{ h }In a right angled triangle, the ratio of its side and the acute angle is the trigonometric ratio of the angles. In this right angled triangle ∠B = 90°. If we take ∠A as an acute angle then –
AB is the base, as the side adjacent to the acute angle.
BC is the perpendicular, as the side opposite to the acute angle.
AC is the hypotenuse, as the side opposite to the right angle.
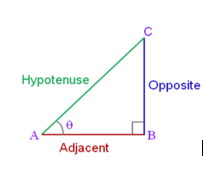
Trigonometric ratios with respect to ∠A: If we take ∠C as acute angle then BC will be base and AB will be perpendicular. Hypotenuse remains the same i.e. AC. So the ratios will be according to that only.
If the angle is same then the value of the trigonometric ratios of the angles remain the same whether the length of the side increases or decreases.
In a right angle triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side so sin A or cos A will always be less than or equal to 1 and the value of sec A or cosec A will always be greater than or equal to 1.
In a right triangle ABC, right-angled at B,
Sin A = (side opposite to angle A)/hypotenuse
Cos A = (side adjacent to angle A)/hypotenuse
Tan A = (side opposite to angle A)/(side adjacent to angle A)
Cosec A = 1/(Sin A) ; Sec A = 1/(Cos A) ; Cot A = 1/(Tan A) ; Tan A = (Sin A)/(Cos A)
If one of the trigonometric ratios of an acute angle is known, the remaining trigonometric ratios of the angle can be easily determined. The values of trigonometric ratios for angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°.
The value of sin A or cos A never exceeds 1, whereas the value of sec A or cosec A is always greater than or equal to 1.
Sin (90° – A) = Cos A, Cos (90° – A) = Sin A; Tan (90° – A) = Cot A, Cot (90° – A) = Tan A; Sec (90° – A) = Cosec A, Cosec (90° – A) = Sec A.